Floating-Point Unit (FPU)
Intro
Why Floating-Point?
STM AN4044| Coding | Dynamic [dB] |
|---|---|
| Int32 | 192 |
| Int64 | 385 |
| Single precision | 1529 |
| Double precision | 12318 |
Floating-Point Unit
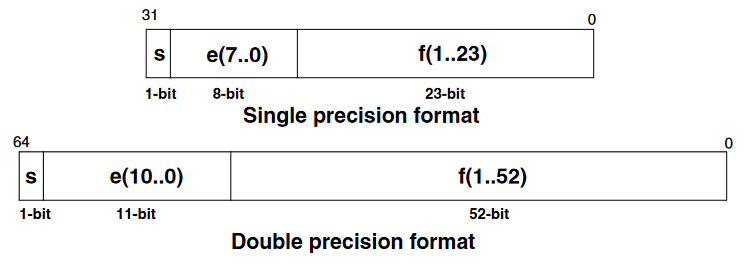
The STM32 ARM Cortex M4F MPUs (e.g. STM32WB, STM32F4, STM32L4) have a single precision floating-point unit. The STM32H7 MPUs have a double precision FPU (not supported yet). Also from STM AN4044- Align the two numbers (have them with the same exponent)
- Perform the operation
- Round out the result
- Code the result
Normalized Numbers Range
| Mode | Exponent | Exp. Bias | Exp. Range | Mantissa | Decimal digits | Min. value | Max. Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single | 8-bit | 127 | -126,+127 | 23-bit | 7.22 | 1.18E-38 | 3.40E38 |
| Double | 11-bit | 1023 | -1022,+1023 | 52-bit | 15.95 | 2.23E-308 | 1.8E308 |
IEEE.754 Single and Double Precision Floating-Point Coding
Some Hints for Using the FPU
It is better to be approximately (vaguely) right than exactly wrong. Carveth Read- Do not use FPU in interrupt service routines.
- Tasks/Threads with FPU operations need much more return stack depth.
- Rounding is not always working properly. useful for precision more than 3.
0.1005e fs. 1.01E-1 ok. 0.1005e fm. 101m ok. 4 set-precision 0.100005e fs. 1.0000E-1 ok. 0.100005e fm. 100.00m ok. 1.00005e f>x x. 1,00004994869232177734375000000000 ok. 1,00005 x. 1,00004999991506338119506835937500 ok.
Some Links
- https://forth-standard.org/standard/float

- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_754

- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single-precision_floating-point_format

- What Every Computer Scientist Should Know About Floating-Point Arithmetic

- Fixed Point
 , https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Q_(number_format
, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Q_(number_format )
)
- https://www.complang.tuwien.ac.at/forth/gforth/Docs-html/Number-Conversion.html#Number-Conversion

- https://www.complang.tuwien.ac.at/forth/gforth/Docs-html/Floating-Point.html#Floating-Point

- https://forth-standard.org/proposals/recognizer#contribution-142

- https://interrupt.memfault.com/blog/cortex-m-rtos-context-switching
 ARM Cortex-M RTOS Context Switching
ARM Cortex-M RTOS Context Switching
- https://mcuoneclipse.com/2019/03/29/be-aware-floating-point-operations-on-arm-cortex-m4f/

- http://support.raisonance.com/content/how-should-i-use-floating-point-unit-fpu-cortex-m4

Floating-Point Words
No separate floating-point stack. A single precision floating-point number is one cell. The 32-bit base-2 format is officially referred to as binary32 IEEE 754-2008Bare FPU Words (Without C Math Library)
f+ ( r1 r2 -- r3 ) Add r1 to r2 giving the sum r3
f- ( r1 r2 -- r3 ) Subtract r2 from r1, giving r3
f* ( r1 r2 -- r3 ) Multiply r1 by r2 giving r3
f/ ( r1 r2 -- r3 ) Divide r1 by r2, giving the quotient r3
fsqrt ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the square root of r1
fabs ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the absolute value of r1
fnegate ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the negation of r1
fround ( r1 -- r2 ) round r1 to an integral value using the "round to nearest" rule, giving r2
fflags@ ( -- u ) get the current value of the Floating Point Status/Control register FPSCR
fflags! ( u -- ) assign the given value to the Floating Point Status/Control register FPSCR
f0= ( r -- ? ) flag is true if r is equal to zero
f0< ( r -- ? ) flag is true if r is less than zero
f< ( r1 r2 -- ? ) flag is true if r1 is less than r2
f~ ( r1 r2 r3 -- ? ) If r3 is positive, flag is true if the absolute value of (r1 minus r2) is less than r3
If r3 is zero, flag is true if the implementation-dependent encoding of r1 and r2 are exactly identical
(positive and negative zero are unequal if they have distinct encodings).
If r3 is negative, flag is true if the absolute value of (r1 minus r2) is less than the absolute value
of r3 times the sum of the absolute values of r1 and r2.
f>s ( r -- n ) n is the single-cell signed-integer equivalent of the integer portion of r
s>f ( n -- r ) r is the floating-point equivalent of the single-cell value n
f>x ( r -- x ) x is the fixed-point equivalent of the floating-point r
x>f ( x -- r ) r is the floating-point equivalent of the fixed-point x
pi ( -- r ) r is pi, approx. 3.14159274101257324
e ( -- r ) r is e, approx. 2.7182818
f. ( r -- ) display, with a trailing space, the floating-point number r in fixed-point notation
precision ( -- u ) return the number of significant digits currently used by F., FE., or FS. as u
set-precision ( u -- ) set the number of significant digits currently used by F., FE., or FS. to u
Words Using the C Math Library
fnumber (a # -- r u ) convert the specified string by a and # to float r, on success u is 1, otherwise 0 >float (a # -- r ? ) convert the specified string by a and # to float r, on success flag is true (more robust) fs. ( r -- ) display, with a trailing space, the floating-point number r in scientific notation fe. ( r -- ) display, with a trailing space, the floating-point number r in engineering notation fm. ( r -- ) display, with a trailing space, the floating-point number r in metric unit prefix notation fsin ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the sine of the radian angle r1 fcos ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the cosine of the radian angle r1 ftan ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the principal radian angle whose tangent is r1 fasin ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the principal radian angle whose sine is r1 facos ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the principal radian angle whose cosine is r1 fatan ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the principal radian angle whose tangent is r1 fsinh ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the hyperbolic sine of r1 fcosh ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the hyperbolic cosine of r1 ftanh ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the hyperbolic tangent of r1 fasinh ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the floating-point value whose hyperbolic sine is r1 facosh ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the floating-point value whose hyperbolic cosine is r1 fatanh ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the floating-point value whose hyperbolic tangent is r1 fceil ( r1 -- r2 ) return the smallest integral value that is not less than r1 ffloor ( r1 -- r2 ) Round r1 to an integral value using the "round toward negative infinity" rule, giving r2 fexp ( r1 -- r2 ) raise e to the power r1, giving r2. f** ( r1 r2 -- r3 ) raise r1 to the power r2, giving the product r3 fln ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the natural logarithm of r1 flog ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the base-ten logarithm of r1
Fixed-Point Words
Fixed-pointd+ ( r1 r2 -- r3 ) add r1 to r2 giving the sum r3 d- ( r1 r2 -- r3 ) subtract r2 from r1, giving r3 x* ( r1 r2 -- r3 ) multiply r1 by r2 giving r3 x/ ( r1 r2 -- r3 ) divide r1 by r2, giving the quotient r3 x. ( r -- ) display, with a trailing space, the fixed-point number r x.n ( r n -- ) print a fixed-point number r with n fractional digits (truncated) x#S ( n1 -- n2 ) Adds 32 comma-digits to number output x# ( n1 -- n2 ) Adds one comma-digit to number output sqrt ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the square root of r1 sin cos tan asin acos atan log2 log10 ln pow2 pow10 exp floor deg2rad ( deg -- rad ) rad2deg ( rad -- deg ) pi pi/2 pi/4 +inf -inf *) fixpt-mat-lib.fs
How to Use
: f|| ( r1 r2 -- r3) 2dup f* -rot f+ f/ ; 27k 100k f|| fm. 21.3k ok.
: f. ( r -- ) \ display, with a trailing space, the floating-point number r in fixed-point notation
$3F000000 \ .5
precision 0 do
$41200000 f/ \ 10.0 /
loop
f+ \ round
f>x
<#
0 #s 2drop \ integer part
46 hold< \ decimal point
precision 0 do
x# \ fract digit
loop
dup
#>
type space
;

This work by Peter Schmid is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
| I | Attachment | History | Action | Size | Date | Who | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Float_example-header.png | r1 | manage | 28.2 K | 2022-11-05 - 10:45 | PeterSchmid | |
| |
ieee-754.png | r1 | manage | 12.7 K | 2022-11-02 - 11:52 | PeterSchmid |
Topic revision: r30 - 2022-11-15 - PeterSchmid
Ideas, requests, problems regarding TWiki? Send feedback