Floating-Point Unit (FPU)
Intro
Why Floating-Point?
STM AN4044| Coding | Dynamic [dB] |
|---|---|
| Int32 | 192 |
| Int64 | 385 |
| Single precision | 1529 |
| Double precision | 12318 |
Floating-Point Unit
Also from STM AN4044- Align the two numbers (have them with the same exponent)
- Perform the operation
- Round out the result
- Code the result
Normalized Numbers Range
| Mode | Exponent | Exp. Bias | Exp. Range | Mantissa | Decimal digits | Min. value | Max. Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
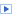
| Single | 8-bit | 127 | -126,+127 | 23-bit | 7.22 | 1.18E-38 | 3.40E38 |
| Double | 11-bit | 1023 | -1022,+1023 | 52-bit | 15.95 | 2.23E-308 | 1.8E308 |
IEEE.754 Single and Double Precision Floating-Point Coding
Some Links
- https://www.complang.tuwien.ac.at/forth/gforth/Docs-html/Number-Conversion.html#Number-Conversion

- https://www.complang.tuwien.ac.at/forth/gforth/Docs-html/Floating-Point.html#Floating-Point

- https://forth-standard.org/proposals/recognizer#contribution-142

- https://interrupt.memfault.com/blog/cortex-m-rtos-context-switching
 ARM Cortex-M RTOS Context Switching
ARM Cortex-M RTOS Context Switching
- printf("%f", myFloat) f. fe. fs.
- atof() oder strtof() benutzen?
- nur single-precision? (7..8 Dezimalstellen, H7 hat double precision FPU)
- kein eigener Stack
- auf float in ISR verzichten
- _FPU_USED
>float in Gforth engine/support.c verwendet strtod() (strtof() for single precision)
Cell to_float(Char *c_addr, UCell u, Float *rp)
{
/* convertible string := <significand>[<exponent>]
<significand> := [<sign>]{<digits>[.<digits0>] | .<digits> }
<exponent> := <marker><digits0>
<marker> := {<e-form> | <sign-form>}
<e-form> := <e-char>[<sign-form>]
<sign-form> := { + | - }
<e-char> := { D | d | E | e }
*/
Char *s = c_addr;
Char c;
Char *send = c_addr+u;
UCell ndigits = 0;
UCell ndots = 0;
UCell edigits = 0;
char cnum[u+3]; /* append at most "e0\0" */
char *t=cnum;
char *endconv;
Float r;
if (s >= send) /* treat empty string as 0e */
goto return0;
switch ((c=*s)) {
case ' ':
/* "A string of blanks should be treated as a special case
representing zero."*/
for (s++; s<send; )
if (*s++ != ' ')
goto error;
goto return0;
case '-':
case '+': *t++ = c; s++; goto aftersign;
}
aftersign:
if (s >= send)
goto exponent;
switch (c=*s) {
case '0' ... '9': *t++ = c; ndigits++; s++; goto aftersign;
case '.': *t++ = c; ndots++; s++; goto aftersign;
default: goto exponent;
}
exponent:
if (ndigits < 1 || ndots > 1)
goto error;
*t++ = 'E';
if (s >= send)
goto done;
switch (c=*s) {
case 'D':
case 'd':
case 'E':
case 'e': s++; break;
}
if (s >= send)
goto done;
switch (c=*s) {
case '+':
case '-': *t++ = c; s++; break;
}
edigits0:
if (s >= send)
goto done;
switch (c=*s) {
case '0' ... '9': *t++ = c; s++; edigits++; goto edigits0;
default: goto error;
}
done:
if (edigits == 0)
*t++ = '0';
*t++ = '\0';
assert(t-cnum <= u+3);
r = strtod(cnum, &endconv);
assert(*endconv == '\0');
*rp = r;
return -1;
return0:
*rp = 0.0;
return -1;
error:
*rp = 0.0;
return 0;
}
#endif
Floating-Point Words
Bare FPU Words (Without C Math Library)
f+ ( r1 r2 -- r3 ) Add r1 to r2 giving the sum r3.
f- ( r1 r2 -- r3 ) Subtract r2 from r1, giving r3.
f* ( r1 r2 -- r3 ) Multiply r1 by r2 giving r3.
f/ ( r1 r2 -- r3 ) Divide r1 by r2, giving the quotient r3.
fsqrt ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the square root of r1.
fabs ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the absolute value of r1.
fnegate ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the negation of r1.
f0= ( r -- ? ) flag is true if and only if r is equal to zero
f0< ( r -- ? ) flag is true if and only if r is less than zero
f< ( r1 r2 -- ? ) flag is true if and only if r1 is less than r2
f~ ( r1 r2 r3 -- ? ) If r3 is positive, flag is true if the absolute value of (r1 minus r2) is less than r3
If r3 is zero, flag is true if the implementation-dependent encoding of r1 and r2 are exactly identical
(positive and negative zero are unequal if they have distinct encodings).
If r3 is negative, flag is true if the absolute value of (r1 minus r2) is less than the absolute value
of r3 times the sum of the absolute values of r1 and r2.
f>s ( r -- n ) n is the single-cell signed-integer equivalent of the integer portion of r.
s>f ( n -- r ) r is the floating-point equivalent of the single-cell value n.
f>fx ( r -- d ) d is the fixed-point equivalent of the floating-point r
fx>f ( d -- r ) r is the floating-point equivalent of the fixed-point d.
f. ( r -- ) Display, with a trailing space, the top number using fixed-point notation:
fx*
fx/
Words Using C Math Library
fsin ( r1 -- r2 ) r2 is the sine of the radian angle r1

This work by Peter Schmid is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
| I | Attachment | History | Action | Size | Date | Who | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
ieee-754.png | r1 | manage | 12.7 K | 2022-11-02 - 11:52 | PeterSchmid |
Topic revision: r13 - 2022-11-02 - PeterSchmid
Ideas, requests, problems regarding TWiki? Send feedback